The prostheses are introduced in a corrosive environment, they are in contact with biological fluids, there may be friction with other materials… and all this causes wear. Hence, plasma coating, in our case of hydroxyapatite or titanium, is presented as a solution to improve the biological response of these components and extend their useful life.
What is Plasma Coating
Plasma coating is an application that uses plasma to modify the properties of materials and coat a surface, which can be rendered hydrophobic or hydrophilic, corrosion resistant, or functionalized to allow bonding.
Of course, medical device manufacturing has used this technique to bring about changes in the performance of materials: optimizing friction and resistance, wetting a surface, or functionalizing it with a specific molecular structure, among other options.
Advantages of plasma coating of hydroxyapatite or titanium
In the specific case of hydroxyapatite or titanium plasma coating of prostheses, we would highlight the following five advantages:
- Greater resistance to wear.
- High hardness and fixation.
- Good antibacterial properties.
- Low coefficient of friction.
- Promotes osseointegration.
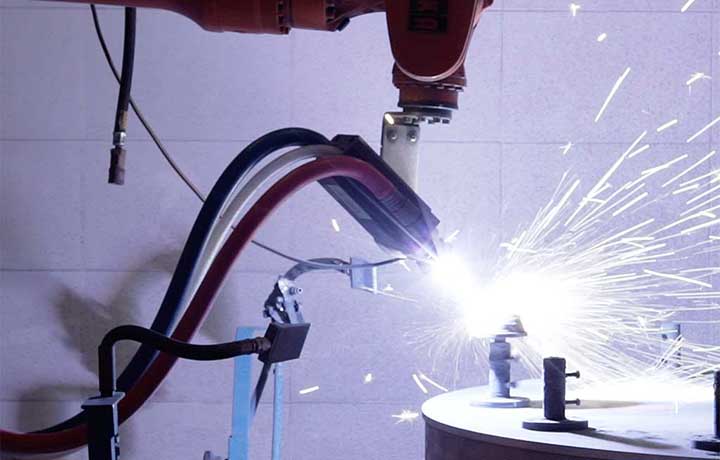
Plasma coating is performed by thermal spray. It is a technology used in the manufacture of parts that consists of spraying small hot, molten or semi-molten particles to adhere them to a surface.
It is a surface coating of a piece or a specific part of the implant to promote osseointegration. Superficial because the thickness is several hundred nanometers (a nanometer is equivalent to one millionth of a millimeter), an ultra-thin layer but with great advantages for the proper functioning of the prosthesis.
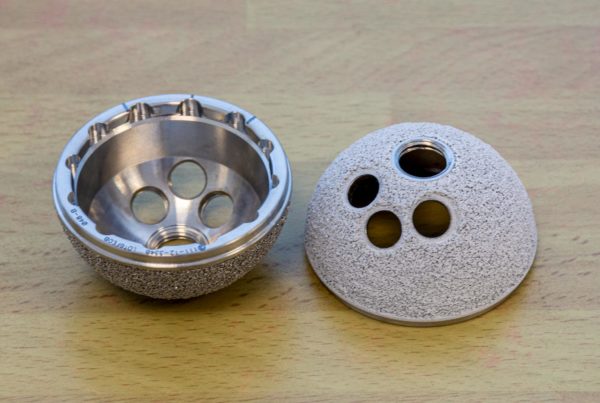
Biovac Plasma Coating Types
At Biovac we carry out plasma coating of three types: titanium, hydroxyapatite and both. Each of them responds to specific needs and has its benefits.
For example, rough titanium coating. This generates a rough surface so that the bone can be well gripped and thus guarantee the fixation of the prosthesis, with excellent bond strength.
It also allows bone growth in the gaps of the coating creating a firm fixation between the implant and the tissues and contains an improved specific surface for osseointegration.
With regard to hydroxyapatite-coated prostheses, they improve the growth of bone tissue through the coating and offer good mechanical stability in the implant fixation process. It should not be forgotten that hydroxyapatite, a calcium phosphate ceramic, is a bioactive material, it can be integrated into bone structures and support their growth without breaking or dissolving.
In addition, hydroxyapatite has the ability to accelerate the reconstruction of bone tissue on the surface of the metallic implant, creating a rapid union and facilitating the interaction between the implant and body tissues to form living bone tissue (bone integration).
For its part, the titanium and hydroxyapatite plasma coating combines the advantages of the previous two. The roughness of titanium and the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite accelerate bone reconstruction on the implant surface, ensuring rapid union with bone tissue and producing stable anchorage and firm fixation of the prosthesis.
Need more information?
Contact Biovac if you have any questions. We will be pleased to help you.